by jsendak | Aug 19, 2025 | AI
arXiv:2508.11836v1 Announce Type: new
Abstract: World models are defined as a compressed spatial and temporal learned representation of an environment. The learned representation is typically a neural network, making transfer of the learned environment dynamics and explainability a challenge. In this paper, we propose an approach, Finite Automata Extraction (FAE), that learns a neuro-symbolic world model from gameplay video represented as programs in a novel domain-specific language (DSL): Retro Coder. Compared to prior world model approaches, FAE learns a more precise model of the environment and more general code than prior DSL-based approaches.
Expert Commentary
World modeling in artificial intelligence is a crucial aspect of developing intelligent agents that can navigate and interact with their environments effectively. In the realm of reinforcement learning, where agents learn through trial and error, having an accurate and efficient world model is essential for making informed decisions. The concept of world models as compressed spatial and temporal representations of an environment is a multi-disciplinary one, drawing from fields such as computer science, cognitive science, and neuroscience.
The use of neural networks in learning these world models presents challenges in terms of transferability and explainability. Neural networks are black box models that can be difficult to interpret, making it hard to understand how the learned representation corresponds to the actual environment dynamics. The proposed approach, Finite Automata Extraction (FAE), offers a novel solution by learning a neuro-symbolic world model from gameplay video using a domain-specific language called Retro Coder.
Neuro-symbolic Approach
Neuro-symbolic approaches combine neural networks with symbolic reasoning to leverage the strengths of both paradigms. By incorporating symbolic reasoning into the learning process, FAE aims to create a more precise and interpretable world model compared to traditional neural network-based approaches. The use of Retro Coder as a domain-specific language allows for the representation of gameplay video as programs, bridging the gap between the raw video data and a symbolic understanding of the environment.
Generalization and Precision
One of the key advantages of FAE is its ability to learn a more general code that captures the underlying structure of the environment. By extracting finite automata from gameplay video, FAE can identify patterns and regularities in the environment that might be missed by traditional neural network models. This capacity for generalization enables agents to make more robust decisions in novel situations, improving their overall performance in complex environments.
Overall, the integration of neuro-symbolic techniques with domain-specific languages represents an exciting development in the field of world modeling. By combining insights from neuroscience, computer science, and artificial intelligence, researchers are pushing the boundaries of what is possible in terms of creating intelligent agents that can understand and interact with their environments in a more human-like manner.
Read the original article
by jsendak | Aug 19, 2025 | GR & QC Articles
arXiv:2508.11714v1 Announce Type: new
Abstract: We consider the self-gravitating Dirac field with a scalar fermion self-interaction term. For strong enough attractive fermion self-interaction, the maximum Arnowitt-Deser-Misner mass of soliton solutions consisting of two fermions can exceed the limit of noninteracting Dirac stars classically, and the “particle-like” solutions of the system can exhibit multiplicity, multiple valid solutions for a single set of parameters, that is inherent in the nonlinear Dirac field. We also find the mass-scale separation in our system similar to that discussed in the Einstein-Dirac-Higgs system. Interestingly, the system admits parity-violated solutions. The broken parity symmetry can be restored by increasing the central redshift of the solution.
Future Roadmap
Based on the conclusions of the study, readers can look forward to the following opportunities and challenges in the field of self-gravitating Dirac fields with scalar fermion interactions:
Opportunities:
- Exploration of soliton solutions consisting of two fermions with strong attractive self-interaction.
- Potential for soliton solutions to exceed the Arnowitt-Deser-Misner mass limit of noninteracting Dirac stars.
- Discovery of multiple valid “particle-like” solutions for a single set of parameters, showcasing the nonlinear nature of the Dirac field.
- Mass-scale separation phenomenon similar to the Einstein-Dirac-Higgs system, offering insights into the behavior of the system.
- Possibility of studying parity-violated solutions and their restoration by increasing the central redshift of the solution.
Challenges:
- Verification of theoretical predictions through experimental observations or simulations.
- Understanding the underlying mechanisms that allow soliton solutions to exceed mass limits and exhibit multiplicity.
- Investigating the implications of mass-scale separation on the overall dynamics of the system.
- Exploring the practical applications of parity-violated solutions and their restoration in real-world scenarios.
Overall, the future roadmap for researchers in this field involves delving deeper into the implications of the study’s conclusions, addressing the challenges posed, and leveraging the opportunities presented to further our understanding of self-gravitating Dirac fields with scalar fermion interactions.
Read the original article
by jsendak | Aug 19, 2025 | Computer Science
Expert Commentary
As an expert in the music industry, I find this project fascinating and highly relevant to the modern landscape of music streaming and consumption. The ability to predict a song’s chart success based on its musical characteristics and early engagement data could revolutionize the way artists and record labels approach marketing, investment decisions, and artistic direction.
The use of machine learning models such as Logistic Regression, K Nearest Neighbors, Random Forest, and XGBoost to predict chart success is a powerful tool in the hands of music industry professionals. The high accuracy rates achieved by the Random Forest and XGBoost models are particularly impressive, pointing to the potential of these models in predicting future hits.
What is especially interesting is the finding that models trained solely on audio attributes can retain predictive power even without factoring in stream count and rank history. This suggests that the musical characteristics of a song play a significant role in its success on streaming platforms like Spotify. This could have major implications for A&R scouting, playlist optimization, and hit forecasting in the music industry.
Overall, this project highlights the importance of data-driven decision-making in the music industry and the potential of machine learning models to provide valuable insights that can shape the future of music marketing and production.
Read the original article
by jsendak | Aug 19, 2025 | Cosmology & Computing
As technology continues to advance at an exponential rate, the future of computing is looking more and more promising with the development of quantum computing. Quantum computing is a revolutionary new approach to processing information that has the potential to completely transform the way we solve complex problems and perform calculations.
Traditional computers operate using bits, which are binary units of information that can either be a 0 or a 1. Quantum computers, on the other hand, use quantum bits, or qubits, which can exist in multiple states at the same time thanks to the principles of quantum mechanics. This allows quantum computers to perform calculations at speeds that are exponentially faster than even the most powerful supercomputers today.
One of the key advantages of quantum computing is its ability to solve complex problems that are currently beyond the capabilities of classical computers. For example, quantum computers have the potential to revolutionize fields such as cryptography, drug discovery, and artificial intelligence by quickly and efficiently solving complex equations and simulations.
In addition to its speed and power, quantum computing also has the potential to significantly reduce energy consumption. Traditional computers generate a significant amount of heat due to the energy required to power and cool them, whereas quantum computers operate at much lower temperatures and can potentially be more energy-efficient.
Despite the incredible potential of quantum computing, there are still many challenges that need to be overcome before it becomes a mainstream technology. One of the biggest challenges is the issue of quantum decoherence, which refers to the loss of quantum information due to interactions with the environment. Researchers are actively working on developing error correction techniques to mitigate this issue and make quantum computing more reliable.
Another challenge is the scalability of quantum computers. Currently, quantum computers are limited in terms of the number of qubits they can support, which limits their computational power. Researchers are working on developing larger and more stable quantum systems to overcome this limitation and make quantum computing more practical for real-world applications.
Despite these challenges, the future of computing looks incredibly promising with the development of quantum computing. As researchers continue to make advancements in this field, we can expect to see quantum computers revolutionize industries and solve some of the world’s most complex problems. The possibilities are truly endless with quantum computing, and the future is looking brighter than ever.

by jsendak | Aug 19, 2025 | Science
Last month, we hosted a special stakeholder event to celebrate the launch of ReelBFD: Digital Arts, Bradford Stories, as part of the Bradford Digital Creatives project. The exhibition showcases the creativity of students from six Bradford schools working with professional digital artists to tell new stories about themselves, their pasts and their futures.
Guests enjoyed an exclusive preview of the exhibition, had the chance to meet the students and professional artists behind the work, and viewed the students’ own short films in the cinema.
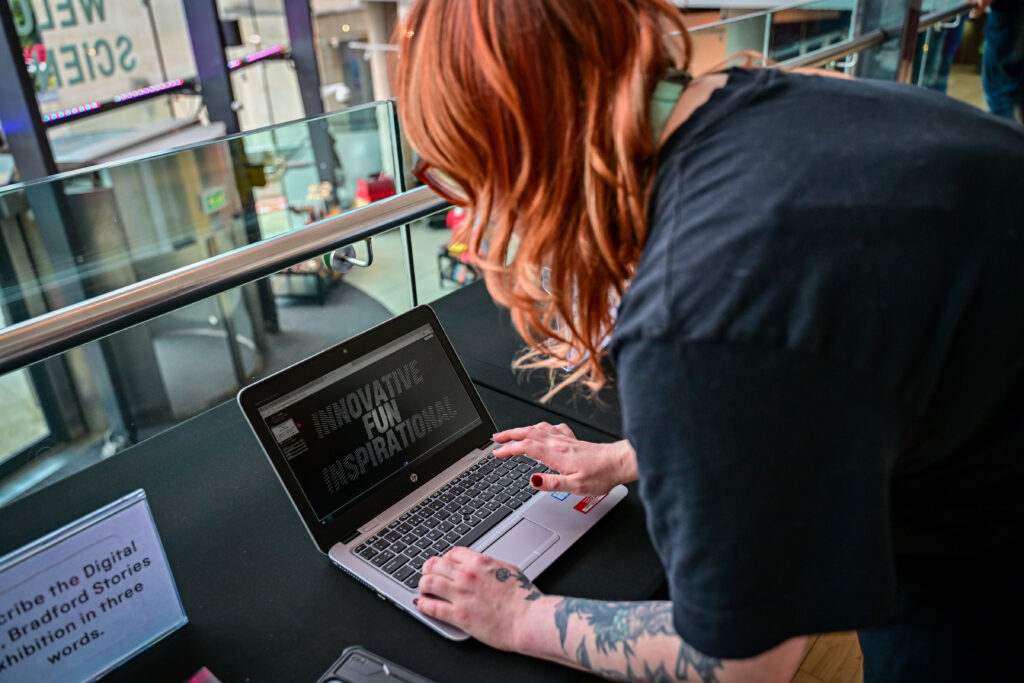
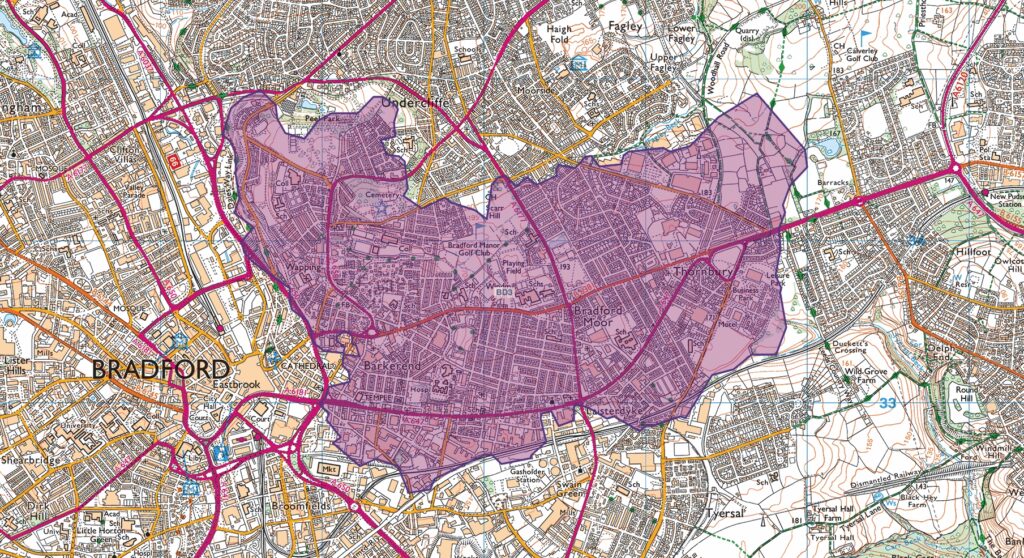
A highlight of the evening was an interactive digital art experience led by artist Emma Tominey—capturing the project’s spirit of co-creation and collaboration through digital artforms. After exploring the exhibition, guests were invited to create their own animated word art on laptops, summing up their personal response to ReelBFD in just three words. These individual animations were collated into a single showreel and overlaid onto six large-scale posters of maps showing the six Bradford postcode areas where participating schools are based. The maps now come to life using Augmented Reality via the Artivive app (on phone or tablet), as guests’ word art animates over the city’s geography.

The AR posters are being distributed to the participating schools, giving them the chance to create their own interactive displays and bring digital art and storytelling directly into their school communities.

Try It Yourself!
Want to see the magic in action? It’s easy:
- Download the free Artivive app from the App Store or Google Play Store.
- Open the app and hover your camera over the map of BD3 below.
- Watch as guests’ feedback and reflections from ReelBFD transform into an animation!

About Bradford Digital Creatives
Bradford Digital Creatives is a two-year pilot project led by the National Science and Media Museum with partners including Born in Bradford (Age of Wonder), Bradford Council, Bradford 2025 UK City of Culture, and Bradford Cultural Education Partnership.
Together, we’re working with over 1,800 teenagers across six Bradford schools to co-create artwork using 360-video, audio storytelling, videogames, and other digital forms. The project is part-funded by Arts Council England and will culminate in a public showcase as part of Bradford 2025 UK City of Culture.
By introducing students to new artforms and professional artists, the project aims to expand cultural participation, develop digital talent, and help young people tell their own Bradford stories in new and exciting ways.
Discover the ReelBFD exhibition and the wider Bradford Digital Creatives project on our website.
Follow along using #ImADigitalCreative and #LetsCreate.