by jsendak | May 5, 2025 | AI
arXiv:2505.00733v1 Announce Type: new
Abstract: Autonomous robots must operate in diverse environments and handle multiple tasks despite uncertainties. This creates challenges in designing software architectures and task decision-making algorithms, as different contexts may require distinct task logic and architectural configurations. To address this, robotic systems can be designed as self-adaptive systems capable of adapting their task execution and software architecture at runtime based on their context.This paper introduces ROSA, a novel knowledge-based framework for RObot Self-Adaptation, which enables task-and-architecture co-adaptation (TACA) in robotic systems. ROSA achieves this by providing a knowledge model that captures all application-specific knowledge required for adaptation and by reasoning over this knowledge at runtime to determine when and how adaptation should occur. In addition to a conceptual framework, this work provides an open-source ROS 2-based reference implementation of ROSA and evaluates its feasibility and performance in an underwater robotics application. Experimental results highlight ROSA’s advantages in reusability and development effort for designing self-adaptive robotic systems.
Expert Commentary:
The development of autonomous robots capable of operating in diverse and uncertain environments poses significant challenges in terms of software architecture and decision-making algorithms. Traditional approaches may struggle to handle the complexity of these systems, as different tasks and environmental conditions require unique logic and configurations.
ROSA, the new knowledge-based framework for RObot Self-Adaptation, addresses this issue by allowing robotic systems to adapt their task execution and software architecture in real-time based on their context. This concept not only enhances the flexibility and efficiency of robotic systems but also opens up opportunities for multi-disciplinary collaboration.
By integrating knowledge modeling and reasoning techniques, ROSA enables task-and-architecture co-adaptation (TACA) in robotic systems. This approach reflects the growing trend towards integrating diverse disciplines such as artificial intelligence, robotics, and knowledge engineering to tackle complex challenges in autonomous systems.
The open-source ROS 2-based reference implementation of ROSA provides an accessible platform for researchers and developers to explore the capabilities of self-adaptive robots. The feasibility and performance evaluation in an underwater robotics application demonstrate the practical advantages of ROSA, including reusability and reduced development effort.
Overall, the innovative approach of ROSA demonstrates the potential for advancing the field of autonomous robotics through the integration of knowledge-based systems and adaptive technologies. This work exemplifies the importance of multi-disciplinary collaboration in designing complex robotic systems capable of addressing dynamic and uncertain environments.
Read the original article

by jsendak | May 5, 2025 | Art
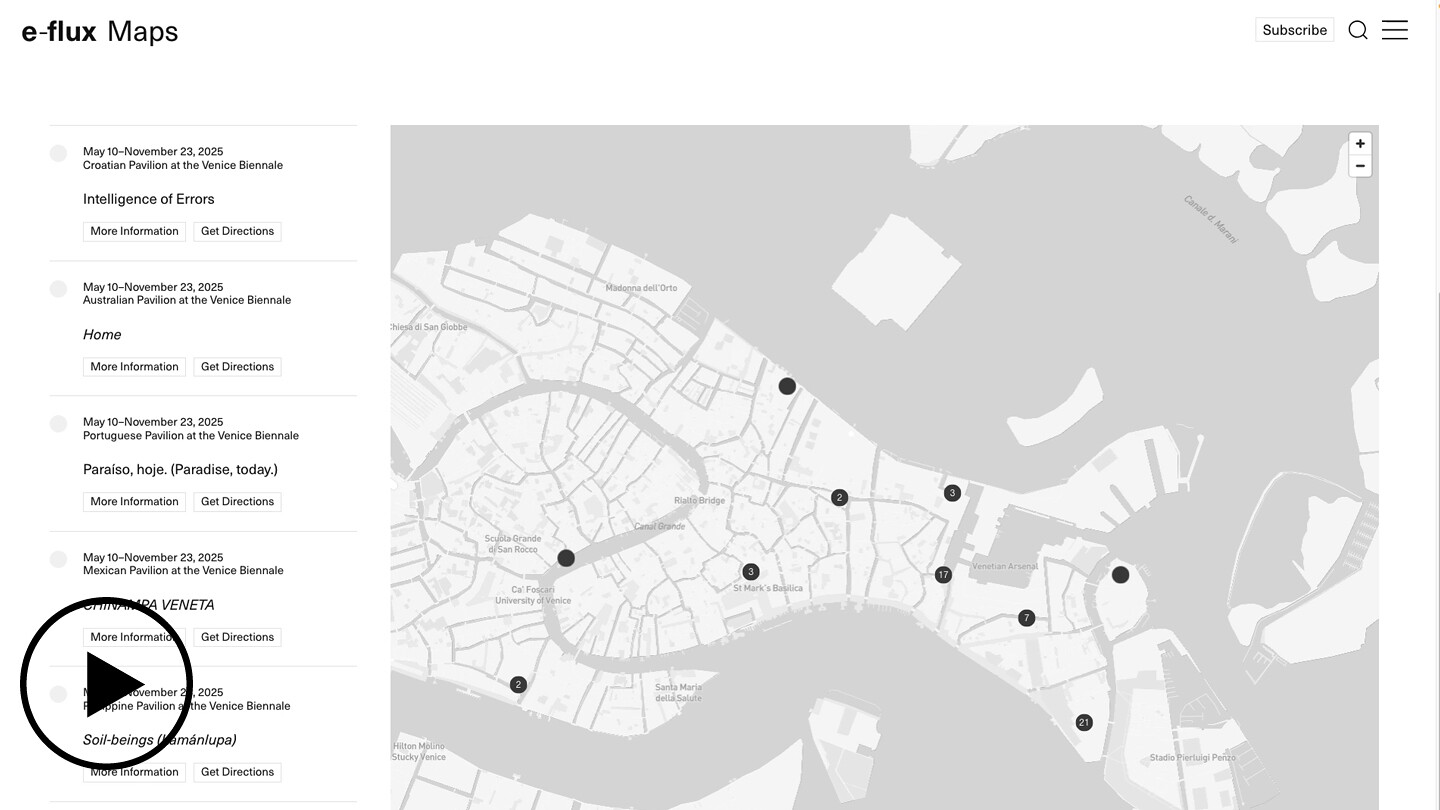
Welcome to the Venice Architecture Biennale e-flux map
The Venice Architecture Biennale has long been a cultural event that captivates the architectural world, drawing in professionals and enthusiasts from around the globe. As we prepare for the 2025 edition of this prestigious exhibition, it is worth reflecting on the historical significance and contemporary relevance of this biennial showcase of innovative design and architectural thinking.
A Legacy of Excellence
Since its inception in 1980, the Venice Architecture Biennale has been a platform for architects to push the boundaries of their craft and explore new ideas. The event’s focus on showcasing cutting-edge designs and thought-provoking installations has earned it a reputation as one of the most important architectural events in the world.
Over the years, the Venice Architecture Biennale has hosted work from renowned architects such as Rem Koolhaas, Zaha Hadid, and Frank Gehry, cementing its status as a must-see event for anyone interested in the future of architecture.
Exploring the Theme
Each edition of the Venice Architecture Biennale is centered around a specific theme, which serves as a starting point for participating architects to explore ideas and concepts central to the field. The theme of the 2025 Biennale promises to be no exception, offering a unique lens through which to view contemporary architectural practice.
As we delve into the e-flux map for the 2025 Venice Architecture Biennale, we invite you to join us on a journey through the latest trends, ideas, and innovations in the world of architecture. From sustainable design practices to cutting-edge technologies, this year’s exhibition promises to be a showcase of creativity and ingenuity in the field of architecture.
Join us as we explore the Venice Architecture Biennale e-flux map and discover the future of architecture today.

The Venice Architecture Biennale 2025 e-flux map is your essential guide to the much-anticipated 19th International Architecture Exhibition.
Read the original article

by jsendak | May 4, 2025 | Art
In the years following World War II, Paris was a bustling hub of creativity and innovation, attracting artists from all corners of the globe. Among them was the Cuban-American painter Carmen Herrera, whose journey to the city would prove to be a transformative chapter in her artistic career. From 1948 to 1953, Herrera lived in Paris, immersing herself in the city’s dynamic postwar artistic community.
During this time, Paris was still reeling from the aftermath of the war, but it also pulsated with a newfound energy and a sense of renewal. The city was a melting pot of ideas, attracting a diverse range of artists who sought to break away from traditional artistic norms and explore new forms of expression. The avant-garde movement was in full swing, with artists like Pablo Picasso, Henri Matisse, and Jean Dubuffet leading the charge.
For Herrera, the experience of living in Paris was a revelation. Surrounded by like-minded creatives, she found the perfect environment to explore her own artistic vision and push the boundaries of her work. The city’s vibrant art scene provided her with a wealth of inspiration, influencing her artistic style and encouraging her to experiment with new techniques.
But Paris was not only a place of artistic inspiration for Herrera; it was also a city marked by a complex history. As she walked its streets, she couldn’t help but be reminded of the significant events that had shaped its past. From the grand boulevards that Baron Haussmann had meticulously designed in the 19th century, to the scars left by the German occupation during the war, Paris was a city that bore the weight of its history.
In her work, Herrera sought to capture both the vibrancy of the present and the echoes of the past. She drew upon the geometric forms and clean lines of the modernist movement, while also incorporating elements of Cubism, a style that had emerged in Paris several decades earlier. Through her paintings, Herrera explored the intersection of art and architecture, creating abstract compositions that invited viewers to contemplate not just the surface, but also the space and depth within.
More than half a century has passed since Herrera’s time in Paris, but her artistic journey still resonates with contemporary artists and art enthusiasts. Her ability to merge tradition with innovation, history with modernity, is a testament to the enduring power of art. As we reflect on her time in Paris, we are reminded of the transformative nature of artistic communities and the importance of finding a space where creativity can flourish.

From 1948 to 1953, Carmen Herrera lived in Paris, immersing herself in the city’s dynamic postwar artistic community
Read the original article
by jsendak | May 2, 2025 | AI
arXiv:2505.00018v1 Announce Type: new
Abstract: This position paper critically surveys a broad spectrum of recent empirical developments on human-AI agents collaboration, highlighting both their technical achievements and persistent gaps. We observe a lack of a unifying theoretical framework that can coherently integrate these varied studies, especially when tackling open-ended, complex tasks. To address this, we propose a novel conceptual architecture: one that systematically interlinks the technical details of multi-agent coordination, knowledge management, cybernetic feedback loops, and higher-level control mechanisms. By mapping existing contributions, from symbolic AI techniques and connectionist LLM-based agents to hybrid organizational practices, onto this proposed framework (Hierarchical Exploration-Exploitation Net), our approach facilitates revision of legacy methods and inspires new work that fuses qualitative and quantitative paradigms. The paper’s structure allows it to be read from any section, serving equally as a critical review of technical implementations and as a forward-looking reference for designing or extending human-AI symbioses. Together, these insights offer a stepping stone toward deeper co-evolution of human cognition and AI capability.
Analysis of Human-AI Agent Collaboration: A Multi-disciplinary Approach
In this position paper, the authors critically survey recent empirical developments on human-AI agent collaboration and discuss the existing technical achievements as well as the persisting gaps in this field. One significant observation made is the lack of a unifying theoretical framework that can integrate the diverse studies and effectively tackle open-ended and complex tasks. This highlights the multi-disciplinary nature of the concepts involved in human-AI collaboration.
To address this gap, the authors propose a novel conceptual architecture called the Hierarchical Exploration-Exploitation Net, which integrates the technical aspects of multi-agent coordination, knowledge management, cybernetic feedback loops, and higher-level control mechanisms. This proposed framework aims to bring together contributions from different domains, ranging from symbolic AI techniques and connectionist LLM-based agents to hybrid organizational practices.
The authors stress the importance of revising existing legacy methods and inspiring new work that combines qualitative and quantitative paradigms. By mapping existing contributions onto the proposed framework, researchers and practitioners can gain a comprehensive understanding and identify areas where improvements can be made. The authors believe that this approach will facilitate the co-evolution of human cognition and AI capability.
This paper serves as an invaluable resource for those interested in human-AI symbiosis as it can be read from any section. Readers can use it as a critical review of technical implementations or leverage it as a reference for designing and extending human-AI collaborations. The multi-disciplinary nature of the concepts discussed in this paper highlights the importance of expertise from various fields, such as cognitive science, computer science, and sociology, for a comprehensive understanding of human-AI collaboration.
Expert Insights
The concepts explored in this position paper emphasize the cross-pollination of ideas from different domains in the context of human-AI agent collaboration. This multi-disciplinary approach is crucial as it brings together knowledge and expertise from various fields, enabling a more holistic understanding of the challenges and opportunities in this field.
The proposed Hierarchical Exploration-Exploitation Net framework holds promise in addressing the existing gaps in human-AI collaboration. By incorporating elements of coordination, knowledge management, feedback loops, and control mechanisms, this conceptual architecture provides a structured approach to designing and improving collaborative systems. It encourages researchers to move beyond traditional approaches and explore hybrid organizational practices that effectively combine human and AI capabilities.
The authors’ call for revising legacy methods and inspiring new work that fuses qualitative and quantitative paradigms is essential for the advancement of human-AI collaboration. The combination of these approaches can leverage the strengths of both human cognition and AI capability, leading to more effective and efficient collaborations.
Overall, this position paper serves as a catalyst for further research, encouraging researchers and practitioners to explore the multi-disciplinary nature of human-AI collaboration. By embracing diverse perspectives and integrating knowledge from different fields, we can unlock the full potential of human-AI symbiosis and drive advancements in this rapidly evolving field.
Read the original article
by jsendak | Apr 30, 2025 | Science
Contingency Plans for Safeguarding Important Information: Future Trends and Recommendations
Published online on 30 April 2025, the article titled “Contingency plans are needed to shore up important information” explores the imperative need for organizations to develop robust strategies to protect and preserve essential data. As technology continues to advance, the potential risks and threats to valuable information are also evolving. This article will delve into the key points of the text and provide insights into potential future trends in information security along with recommendations for the industry.
The Growing Significance of Contingency Plans
With the increasing digitization of data and the reliance on technology for various operations, the importance of contingency plans for safeguarding important information has become paramount. The text highlights the vulnerability of critical data in the face of unforeseen events such as cyberattacks, natural disasters, or technical failures. Organizations must acknowledge the potential risks to their data and have robust plans in place to mitigate potential damages.
The need for comprehensive contingency plans has traditionally been associated with sectors such as finance, healthcare, and defense. However, as more industries undergo digital transformation and data becomes integral to their operations, contingency planning becomes a universal necessity. This shift in perception is accentuated by recent high-profile cyberattacks and data breaches that have caused significant financial and reputational damage.
Future Trends in Information Security
As the world becomes increasingly interconnected, it is essential to anticipate the future trends in information security to enhance the effectiveness of contingency plans. The following trends are expected to shape the industry:
- Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning: AI and machine learning algorithms are predicted to play a pivotal role in identifying and preventing potential threats. These technologies can analyze massive datasets, detect patterns, and autonomously respond to malicious activities, significantly enhancing the capabilities of contingency plans.
- Zero Trust Architecture: The traditional perimeter-based security approach is becoming obsolete. Zero Trust Architecture, which assumes that every user or device could be a potential threat, is gaining prominence. This approach strengthens data protection by implementing strict access controls, multi-factor authentication, and continuous monitoring.
- Quantum Cryptography: As quantum computing advances, so does the need for quantum-resistant encryption methods. Quantum cryptography provides a framework for secure communication, leveraging the principles of quantum mechanics to enhance data confidentiality and integrity.
- Blockchain Technology: Blockchain’s distributed and immutable nature makes it an attractive solution for storing and verifying data. Its integration into existing contingency plans can enhance data transparency, traceability, and resistance to tampering.
- Rapid Incident Response: The ability to detect, respond, and recover from incidents will continue to evolve rapidly. With advanced threat intelligence platforms, automated response systems, and real-time monitoring, organizations can minimize the damage caused by cyber threats.
Recommendations for the Industry
To ensure data protection and resilience in the face of future challenges, organizations should consider the following recommendations:
- Regular Risk Assessments: Conducting comprehensive risk assessments will enable organizations to identify potential vulnerabilities and develop appropriate contingency plans specific to their unique requirements.
- Continuous Employee Training: Employees are often the weakest link in information security. Regular training programs can educate employees about potential threats, best practices, and their role in maintaining data security.
- Proactive Monitoring: Implementing robust monitoring systems and security frameworks can help organizations identify and respond to threats promptly, minimizing the damage caused.
- Collaboration for Threat Intelligence: Sharing threat intelligence and collaborating with industry peers can enhance the collective ability to identify and address emerging threats effectively.
- Investing in Emerging Technologies: Keeping abreast of emerging technologies and investing in AI, machine learning, quantum cryptography, and blockchain can significantly enhance data protection capabilities and improve the effectiveness of contingency plans.
In conclusion, the increasing reliance on technology and digitization necessitates the development of comprehensive contingency plans to safeguard important information. The future trends in information security, such as AI and machine learning, Zero Trust Architecture, quantum cryptography, blockchain, and rapid incident response, present opportunities for organizations to strengthen their data protection strategies. By implementing the provided recommendations, organizations can proactively address potential threats and ensure the resilience of their data in an increasingly interconnected world.
References:
– Nature, Published online: 30 April 2025; doi:10.1038/d41586-025-01034-x
– Example Reference 1
– Example Reference 2